Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)
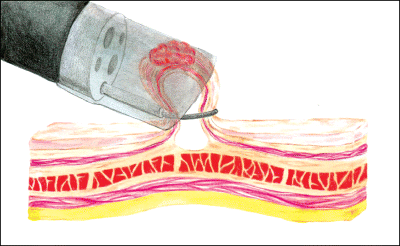
Gastrointestinal endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is a procedure to remove cancerous or other abnormal tissues (lesions) from the digestive tract.
Endoscopic mucosal resection is performed with a long, narrow tube equipped with a light, video camera and other instruments. During EMR of the upper digestive tract, the tube (endoscope) is passed down your throat to reach an abnormality in your esophagus, stomach or upper part of the small intestine (duodenum).
To remove lesions from the colon, the tube is guided up through the anus.
Primarily a treatment procedure, EMR is also used to collect tissues for diagnosis. If cancer is present, EMR can help determine if the cancer has invaded tissues beneath the digestive tract lining.
Endoscopic mucosal resection is a less invasive alternative to surgery for removing abnormal tissues from the lining of the digestive tract. These tissues may be:
Endoscopic mucosal resection is usually performed by a specialist in digestive system disorders (gastroenterologist) who has expertise in this technique.
Risks of the endoscopic mucosal resection include:
Call your doctor or get emergency care if you develop any of the following signs or symptoms after undergoing endoscopic mucosal resection:
There are a few versions of endoscopic mucosal resection. Ask your gastroenterologist about how your procedure will be performed. A common approach includes these steps:
During an endoscopic mucosal resection, you can expect the following:
You’ll remain in a recovery room until most of the effect of the sedative has worn off. You’ll receive written instructions about when you can start eating and drinking and when you can resume normal activities. You’ll be advised not to do any of the following activities until the next day:
Relatively mild side effects may occur within 24 hours after the procedure including:
You’ll also receive written instructions about when to call your doctor or get emergency care after the procedure. The following signs or symptoms may indicate a serious complication from endoscopic mucosal resection:
Typically, a follow-up exam is performed three to 12 months after your procedure to be sure the entire lesion was removed. Depending on the findings, your doctor will advise you about further examinations.
An exam will likely include a visual inspection with the use of an endoscope. Your doctor may mark the area of the removed lesion with ink (tattoo) so that when follow-up endoscopy is performed, he or she can be sure the lesion was removed completely.

Powered by Appointment-Plus
Advanced Gastroenterology, Inc.
Phone: (805) 719-0244
555 Marin Street, Ste. 270
Thousand Oaks, CA 91360